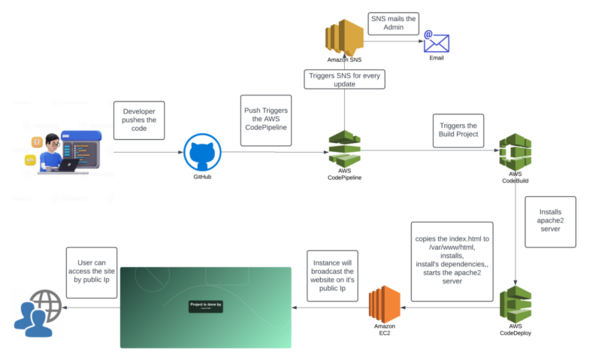
Steps
- Set Up the Repository and Initialize Version Control:
- Start with a clean Git repository (GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket).
- Define a branching strategy (e.g., GitFlow or trunk-based) to control how features are merged.
- Configure CI with Build and Test Automation:
- Set up build automation in Jenkins or GitHub Actions.
- Write unit and integration tests for automated verification at each commit.
- Set Up Automated Deployments for Staging:
- Create staging environments with Docker or Kubernetes.
- Use tools like Helm to manage deployment configurations.
- Manage Secrets and Environment Variables:
- Securely manage secrets using HashiCorp Vault or AWS Secrets Manager.
- Ensure sensitive data is accessible only within the CI/CD pipeline.
- Monitor and Log Each Deployment Stage:
- Integrate monitoring (e.g., Prometheus) to track deployment health.
- Set alerts in Slack or email to notify of successful or failed deployments.
- Configure Rollback Mechanisms:
- Create automated rollback scripts triggered by failed deployments.
- Test rollback and restore functionalities regularly.
Implementing SRE Principles: A Practical Guide for Freelancers
Steps
- Define SLIs, SLOs, and SLAs with Your Clients:
- Understand and negotiate reliability metrics like uptime and latency.
- Align expectations with realistic service-level objectives.
- Set Up Incident Management and On-Call Practices:
- Use PagerDuty or OpsGenie for effective incident alerting and management.
- Establish on-call schedules and incident escalation processes.
- Automate Monitoring and Alerting with Affordable Tools:
- Use open-source monitoring tools (e.g., Prometheus) for metrics collection.
- Create actionable alerts to catch incidents early.
- Establish Error Budgets for Managing Trade-Offs:
- Define acceptable failure rates with clients to prevent burnout.
- Regularly review error budgets to balance reliability and release frequency.
- Optimize with Continuous Learning and Postmortems:
- Document all incidents and hold postmortem analyses.
- Turn insights into actionable improvements, like updated runbooks and automated alerts.
Securing Your DevOps Environment: Tips from DevSecOps Freelancers
Steps
- Secure Source Code Repositories and Access:
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) on GitHub/GitLab accounts.
- Limit repository access using role-based permissions.
- Integrate Static Application Security Testing (SAST):
- Use tools like SonarQube to detect vulnerabilities in code.
- Automate scans to run with each pull request and merge.
- Automate Dependency Checks (DAST):
- Set up automated dependency scanning with tools like Snyk or OWASP Dependency-Check.
- Regularly update dependencies to patch vulnerabilities.
- Implement Infrastructure Security as Code:
- Use Terraform to define infrastructure securely.
- Add security groups, IAM roles, and least-privilege access policies directly in your Terraform code.
- Enforce Secret Management with Secure Storage:
- Replace hardcoded secrets with environment variables stored in Vault or AWS Secrets Manager.
- Audit secrets regularly and rotate them automatically if possible.
Automating Infrastructure with Terraform: A Beginner’s Guide
Steps
- Install Terraform and Set Up Your Environment:
- Download Terraform and set up your preferred editor with the Terraform plugin.
- Configure AWS or other provider credentials for authentication.
- Write Your First Terraform Configuration:
- Start with a simple
main.tfto define resources like EC2 instances, S3 buckets, or networking setups. - Use Terraform modules to organize and reuse code.
- Start with a simple
- Manage State and Use Remote Backends:
- Use a backend like S3 or Terraform Cloud to store state files securely.
- Lock state files during operations to prevent accidental overwrites.
- Use Variables and Outputs for Flexibility:
- Define variables in
.tfvarsfiles for easy configuration across environments. - Use outputs to pass data between modules or export values for other tools.
- Define variables in
- Automate Terraform Workflows with CI/CD:
- Integrate Terraform with CI/CD tools to automatically apply changes.
- Use GitOps to manage infrastructure changes directly from the version control system.
Using Docker and Kubernetes for Efficient DevOps Workflows
Steps
- Containerize Applications with Docker:
- Write Dockerfiles to build lightweight, portable containers for each service.
- Test container images locally before pushing to a container registry.
- Set Up a Kubernetes Cluster:
- Use Minikube or kind for local testing or provision a cloud-managed Kubernetes cluster.
- Understand core concepts: Pods, Services, and Namespaces.
- Define Kubernetes Manifests for Deployment:
- Write YAML files for Deployments, Services, and ConfigMaps.
- Organize and version-control manifest files to standardize deployments.
- Automate Scaling and Load Balancing:
- Configure horizontal pod autoscaling to handle fluctuating workloads.
- Set up a LoadBalancer or Ingress for managing traffic to services.
- Set Up Monitoring and Logging for Kubernetes:
- Use Prometheus and Grafana to monitor application performance and resource usage.
- Implement centralized logging with tools like Fluentd and Elasticsearch.