In this tutorial i’m going to share Top 50 Important Linux Command for users with example.
1. Use of ls -la command.
The ls -la command is used to list detailed information about all files and directories, including hidden ones, in a directory. Here’s a breakdown of its components
ls -l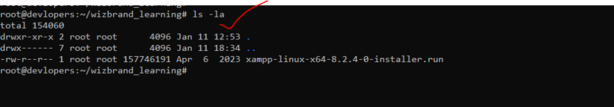
2. Use of cd command
The cd command in Linux is used to change the current working directory. It stands for “change directory”. Here’s how you use it:
cd
3. Use of pwd command
When you execute pwd in a terminal, it will print the full path of the directory you are currently in.
pwd
4. use of mkdir command
The mkdir command in Linux is used to create directories (folders) within the file system. Here’s how you use it:
mkdir amit
5. use of rm file
The rm command in Linux is used to remove files or directories from the file system. Here’s how you use it:
rm file.txt6. Use of cp command
The cp command in Linux is used to copy files and directories from one location to another. Here’s how you use it:
cp file1.txt7. Use of mv command in linux
The mv command in Linux is used to move or rename files and directories. Here’s how you use it:
mv amit.txt /root/sumit8. Use of touch command
The touch command in Linux is used to create new empty files or update the timestamps of existing files. Here’s how you use it:
touch myfile.txt

9. Use of cat command
The cat command in Linux is primarily used to concatenate and display the contents of files. However, it has several other useful functions. Below are some common use cases of the cat command:

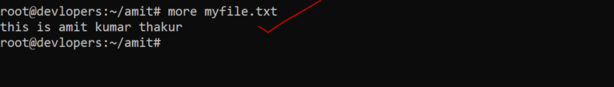
10. Use of More command
The more command in Linux is used to view the contents of a file one page at a time. It is useful for viewing large files or long output that cannot fit on a single screen. Here’s how you can use the more command:
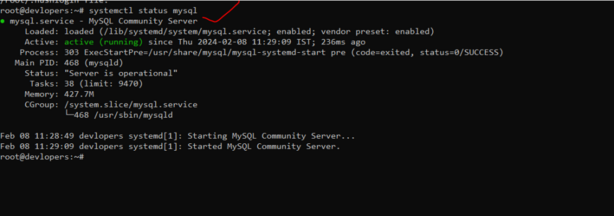
11. Use of systemctl status mysql command
systemctl status mysqlThe systemctl status mysql command is used to check the status of the MySQL service on a Linux system using systemd for managing services. Here’s a breakdown of what each part of the command does:
12. Use of head command in Linux
The head command in Linux is used to display the beginning (head) of a text file or input from another command. By default, it prints the first 10 lines of the specified file or input stream to the standard output. Here’s how you can use the head command:
head myfile.txt
13. Use of Table Command in linux
The tail command in Linux is used to display the end (tail) of a text file or input from another command. By default, it prints the last 10 lines of the specified file or input stream to the standard output. Here’s how you can use the tail command:

14. Use of grep command in Linux
The grep command in Linux is a powerful tool used for searching text patterns within files or streams of text. It stands for “Global Regular Expression Print”. Here’s how you can use the grep command:
grep "pattern" file.txt
15. Use of chmod 755
The chmod command in Linux is used to change the permissions of files and directories. The permissions are represented by three sets of three characters, each indicating the permissions for the file’s owner, the group the file belongs to, and others (everyone else). The number 755 is a shorthand notation used to specify permissions in octal form. Here’s how the chmod 755 command works:
chmod 755 myfile.txt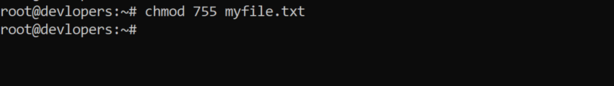
16. Use of tar -cvzf archive.tar.gz command
The tar command in Linux is used to create, manipulate, or extract tar archives. The -cvf options are used together to specify the action to create a new archive (c), display the progress verbosely (v), and specify the file name of the archive (f). Here’s how you can use tar -cvf to create a new tar archive:
tar -cvzf archive.tar.gz myfile.txt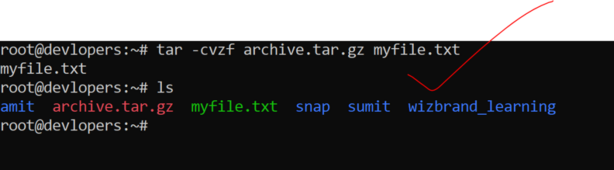
17 Use of gzip command
gzip myfile.txtThe gzip command in Linux is used to compress files. It is frequently used to reduce the size of files and to save disk space. Here’s how you can use the gzip command:
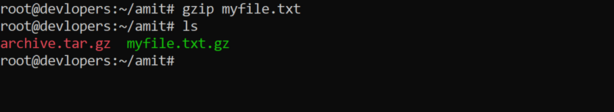
18. Use of gunzip command
The gunzip command in Linux is used to decompress files that have been compressed using the gzip compression algorithm. It is essentially the counterpart to the gzip command for decompression. Here’s how you can use the gunzip command:
gunzip myfile.txt.gz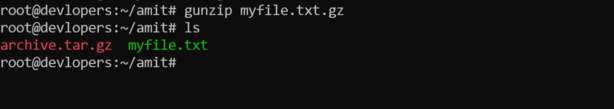
19. use of df -h command
The df command in Linux is used to display disk space usage information for mounted filesystems. The -h option is used to print the output in a human-readable format, which means the sizes are displayed in a more easily understandable format (e.g., KB, MB, GB, etc.). Here’s how you can use the df -h command:
df -h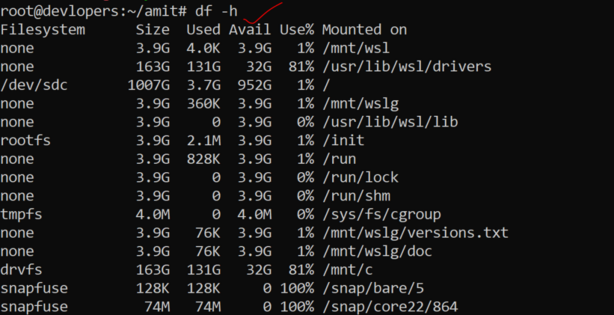
20. Use of du -sh command
The du command in Linux is used to estimate the disk space usage of files and directories. The -s option is used to summarize the usage of each specified file or directory, and the -h option is used to display sizes in a human-readable format. Here’s how you can use the du -sh command:
du -sh
21. Use of free -m command
The free command in Linux is used to display information about the system’s memory usage. The -m option is used to display the output in megabytes. Here’s how you can use the free -m command:
free -m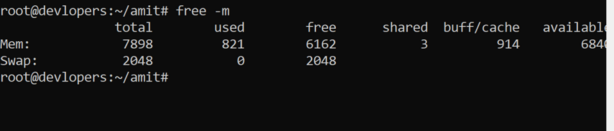
22. Use of ps aux command
ps auxThe ps aux command in Linux is used to display a snapshot of the current processes running on the system. Here’s how you can use ps aux:
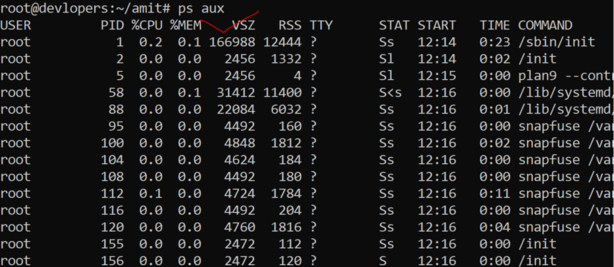
23. Use of shutdown -h now command
The shutdown command in Linux is used to shut down or reboot the system. The -h option is used to specify that the system should be halted (powered off) after shutting down, and the now parameter indicates that the action should be taken immediately. Here’s how you can use the shutdown -h now command to power off the system:
shutdown -h now
24. Use of wget command
The wget command in Linux is used to download files from the internet. It supports downloading files using various protocols, including HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP. Here’s how you can use the wget command:
Example: wget https://example.com/file.txt25. Use of history command
When you run this command, it displays a numbered list of previously executed commands, along with their line numbers, in chronological order, starting from the most recent command.
history